硬质合金厂家-硬质合金与钨钢的区别
标签:硬质合金厂家
硬质合金厂家-金信分享硬质合金与钨钢的区别
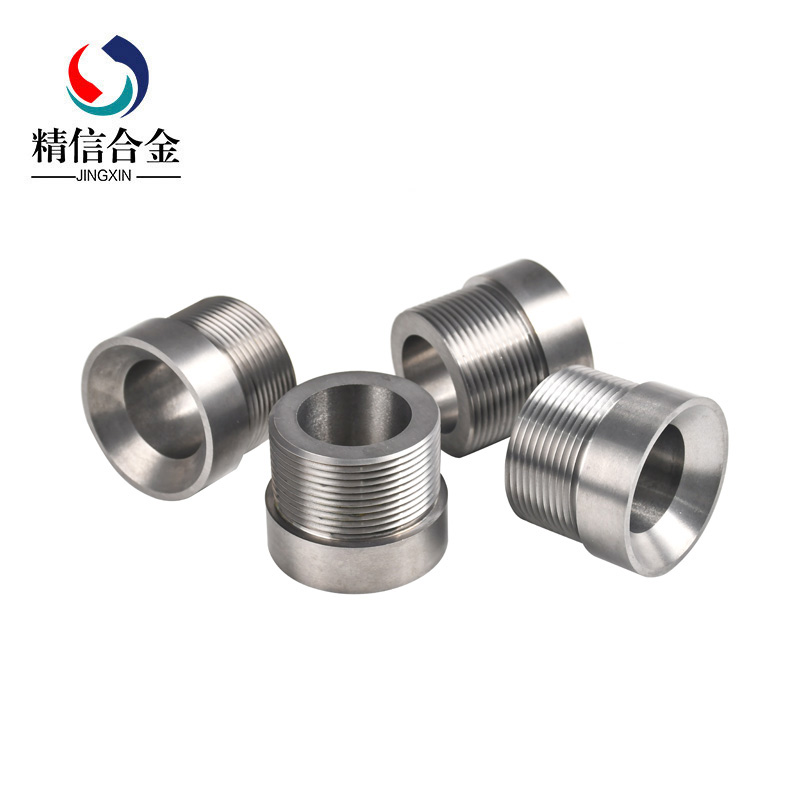
钨钢:成品中约含钨18%合金钢, 钨钢归于硬质合金,又称之为钨钛合金。硬度为维氏10K,仅次于钻石。正因如此,钨钢的商品(多见的有钨钢手表),具有不易被磨损的特性。常用于车床刀具、冲击钻钻头、玻璃刀刀头、瓷砖割刀之上,坚固不怕退火,但质脆。Tungsten steel: The finished product contains about 18% tungsten alloy steel. Tungsten steel belongs to cemented carbide, also known as tungsten-titanium alloy. The hardness is 10K Vickers, second only to diamonds. Because of this, tungsten steel products (most commonly tungsten steel watches) are not easily worn out. Usually used on lathe cutters, impact drills, glass cutters, ceramic tile cutters, strong and not afraid of annealing, but brittle.
硬质合金: 归于粉末冶金领域硬质合金又名金属陶瓷是以金属碳化物(WC、TaC, TiC、NbC等)或许金属氧化物(如Al2O3, ZrO2等)为首要成份,参加适量的金属粉末(Co、Cr、 Mo 、Ni 、Fe等)通过粉末冶金方法制成,具有金属某些特质的陶瓷。
钴(Co)是用来在合金中起粘结效果的,就是在烧结的过程中,它能把碳化钨(WC)粉末包围并紧紧地粘结在一起,冷却后,就成了硬质合金. (效果相当于混凝土中的水泥)。含量通常:3%--30% 碳化钨(WC)是决议此硬质合金或金属陶瓷某些金属性质的首要成份,占总成份 70%---97%(分量比) 广泛用于耐磨,耐高温,耐腐蚀,工作环境恶劣的零件或刀具,工具的刀头上。 钨钢归于硬质合金,但硬质合金纷歧定是钨钢, 如今台湾和东南亚国家的客户喜欢用钨钢这个词,假如跟他们仔细谈深入,咱们会发现,大部分仍是指咱们的硬质合金。。。
钨钢与硬质合金差异在于:又名高速钢或工具钢,钨钢是用炼钢技术在钢水中参加钨铁作钨的质料熔炼而成的,又名高速钢或工具钢,其钨含量通常在15-25%,;而硬质合金是用粉末冶金技术以碳化钨为主体与钴或其它粘结金属一起烧结而成的,其钨含量通常在80%以上。
简略的说一切硬度走超越HRC65的东西只要是合金都可以叫硬质合金Cemented carbides: Cemented carbides (WC, TaC, TiC, NbC, etc.) or metal oxides (such as Al2O3, ZrO 2, etc.) are the main components of cemented carbides, which belong to the field of powder metallurgy. Ceramics with certain characteristics of metals are made by powder metallurgy with appropriate amount of metal powders (Co, Cr, Mo, Ni, Fe, etc.). Porcelain. Cobalt (Co) is used for bonding in alloys. During sintering, it can surround and bond tungsten carbide (WC) powder tightly together. After cooling, it becomes cemented carbide. (The effect is equivalent to cement in concrete). Usually: 3%-30% tungsten carbide (WC) is the primary component to determine the properties of some metals of this cemented carbide or cermet, accounting for 70%-97% of the total composition. It is widely used in wear-resistant, high temperature-resistant, corrosion-resistant parts or tools, tool heads in harsh working environment. Tungsten steel belongs to cemented carbide, but the cemented carbide is different from tungsten steel. Now customers inTaiwanand Southeast Asian countries like to use the word tungsten steel. If we talk with them carefully, we will find that most of them still refer to our cemented carbide. Tungsten steel differs from cemented carbide in that tungsten steel, also known as high-speed steel or tool steel, is melted by steelmaking technology in which ferrotungsten is used as tungsten material in molten steel. Also known as high-speed steel or tool steel, its tungsten content is usually 15-25%. Cemented carbide is a powder metallurgy technology with tungsten carbide as the main body and cobalt or other bonded metals. When sintered together, the tungsten content is usually more than 80%. Briefly speaking, anything harder than HRC65 can be called cemented carbide as long as it is an alloy.
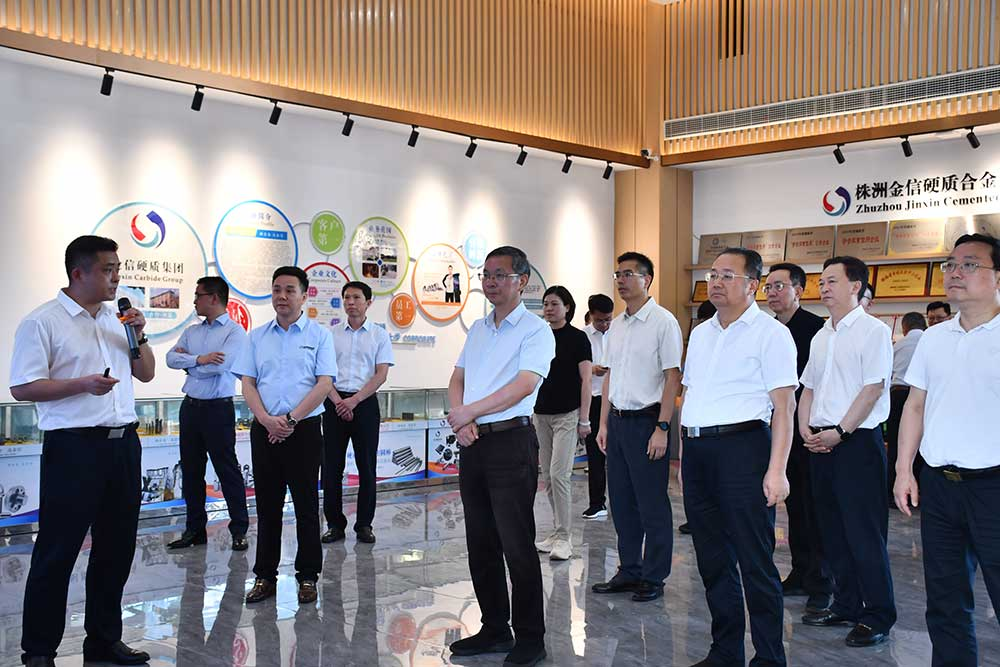

金信硬质集团被纳入2024年株洲重点观摩项目
亮进度、晒成绩!2024年株洲市打造“三个高地”二季度讲评会之重点项目观摩活动举行,市委书记曹慧泉,市委副书记、市长陈恢清分别率队观摩。市领导何恩广、刘光跃、聂方红、杨英杰、江小忠、罗绍昀、刘亚亮、罗
2024/8/12
- 株洲金信喊你过端午!粽香里的企业温度,与你共赴美好 “食” 光~2025/5/30
- 硬质合金阀座:高压密封场景的耐磨核心解决方案2025/5/27
- 五一劳动节 | 致敬每一位奋斗的金信人2025/5/12
- 钨钢和高钨合金它们之间的区别2025/4/29
- 【调研指导促发展】新华社及市委宣传部一行莅临株洲金信调研硬质合金生产创新成果2025/3/8
 jinxin015@ojinxin.com
jinxin015@ojinxin.com  15886350026
15886350026